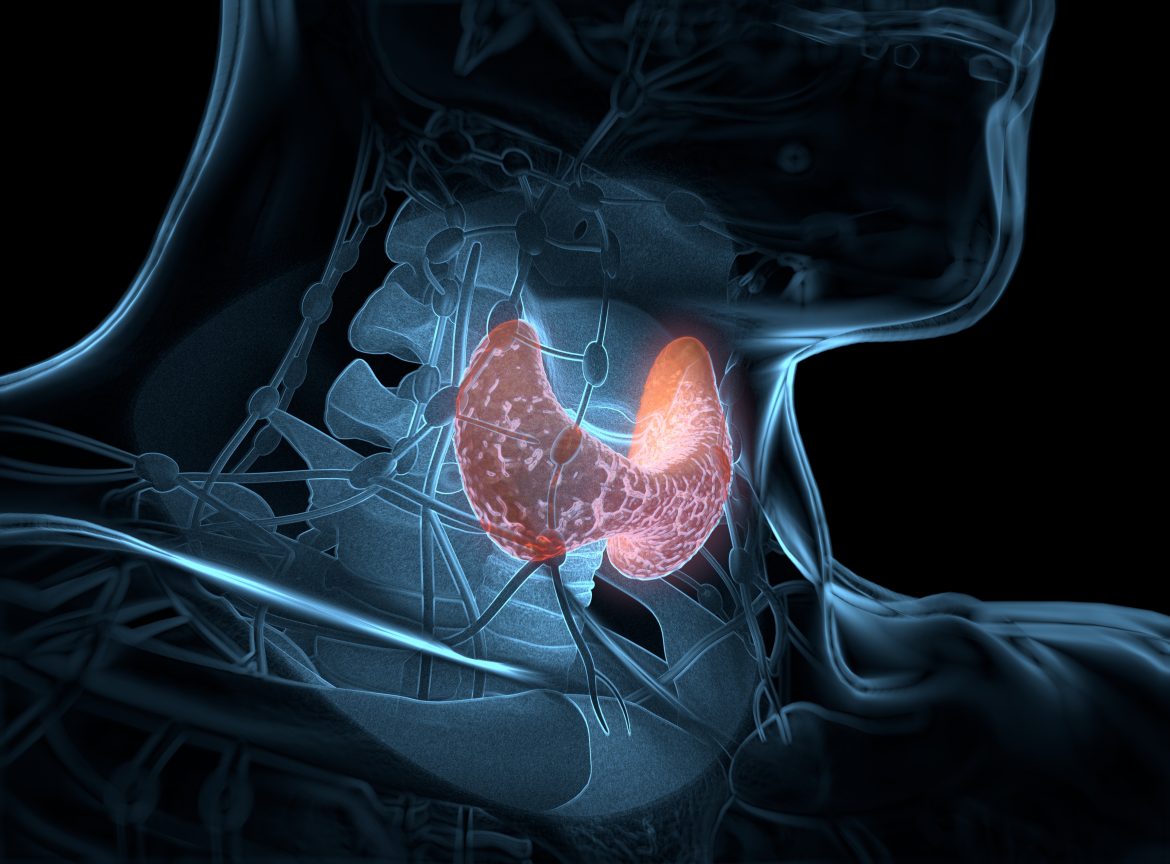
Thyroid cancer accounts for 1% in the structure of all oncopathologies, and it accounts for less than 0.5% of deaths. The disease can occur at any age. The maximum number of cases of a tumor of such localization was registered in persons from 45 to 64 years old, however, the most malignant thyroid cancer occurs in childhood and puberty.
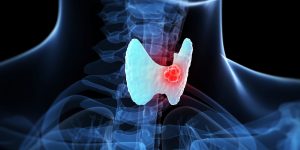
What factors increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer?
The effect of radiation on the cervical region, where this endocrine organ is located
The presence of this pathology in close blood relatives
Work in hazardous production: hot shops, metallurgical plants, as well as workers in X-ray rooms
Constant stress that has a destructive effect on the body’s defenses
The negative effects of tobacco and alcoholic beverages
Chronic endocrine diseases: lesions of the thyroid gland itself, pituitary and hypothalamus, ovaries in women
The presence of these factors does not mean 100% of the likelihood of developing an oncological process, however, it requires preventive examinations and careful monitoring of your health.
What are the symptoms of thyroid cancer?
It is necessary to regularly conduct self-examinations of the anterior surface of the neck. If a subcutaneous nodule or an enlarged lymph node is found, it is imperative to consult a specialist!
With cancer of the thyroid gland, symptoms associated with a violation of the synthesis of the hormone thyroxine may occur.
With excessive hormone production:
Dramatic weight loss with good appetite
Excessive sweating
Shaking hands
Increased excitability, anxiety
Interruptions in the work of the heart: increased heart rate, arrhythmias, increased blood pressure
With insufficient production of thyroxine:
Noticeable weight gain in the absence of appetite
Slowness, drowsiness, constant fatigue
Decreased heart rate, temperature, arterial hypotension
Dry skin, hair loss, brittle nails
With an increase in the size of the tumor, symptoms associated with compression or damage to neighboring organs may appear:
Swallowing disorder
Foreign body feeling in the throat
Voice change
Dry, excruciating cough
Feeling short of air
Treatment for thyroid cancer
Like any other oncological process, thyroid cancer requires an integrated approach to treatment.
The main and main method is surgical treatment. Removal of the affected portion of the thyroid gland preserves intact glandular tissue, thus eliminating lifelong hormone replacement therapy.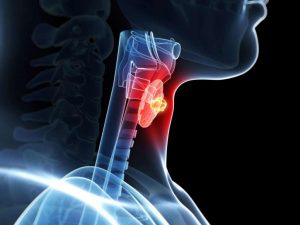
Radioactive iodine therapy has been used quite successfully for the treatment of thyroid cancer for a long time. Iodine selectively accumulates in her tissue and destroys tumor cells. This method of treatment does not entail serious consequences for the body, however, the received radioactive dose has a negative effect on healthy tissues.
The use of tablet forms of thyroid hormone allows you to simultaneously achieve two goals: to restore hormonal imbalance that has arisen in the body, and also to stop the growth of atypical cells.
Radiation therapy can be considered as a comprehensive treatment for thyroid cancer. However, it is usually not used, but replaced by radioactive iodine therapy. Radiation therapy is not inferior in effectiveness, but it can lead to a large number of complications.
Photodynamic therapy, which is used both independently and in the complex therapy of thyroid cancer https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_cancer, can achieve a good result. The photosensitizer drug accumulates only in atypical cells. Under the influence of a special light source, the photosensitizer is destroyed and releases substances that kill tumor formation.