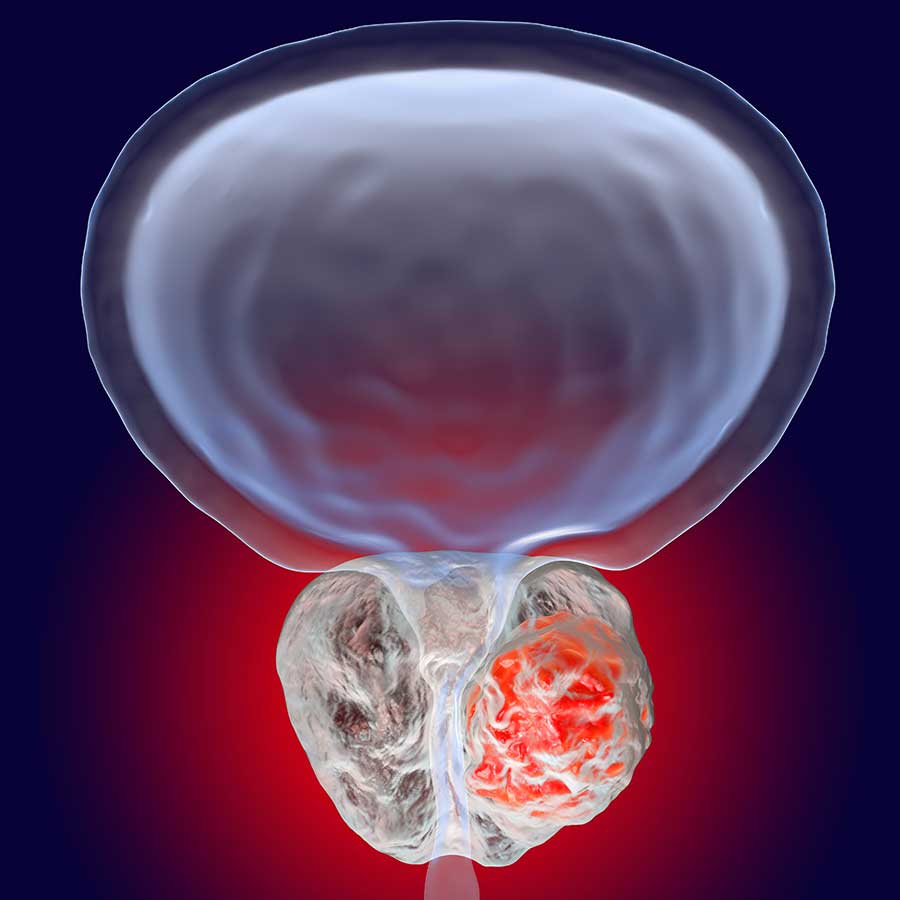
Prostate cancer is one of the main medical and social problems of oncourology. Lesions of the prostate gland of various nature and etiology are observed in 90% of the male population over 40 years of age. And the average age of people who are diagnosed with a malignant neoplasm is 60-70 years. The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the difficulty of differentiating a benign process from a malignant one at the initial stage. Prostate cancer does not have vivid, specific clinical symptoms. That is why the overwhelming majority of patients seek help from specialists in the later stages.
Symptoms of the disease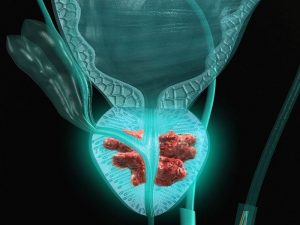
It is important to remember that the earlier prostate cancer is detected, the more effective the treatment will be. What symptoms require a visit to a specialist?
Dysuria – Difficulty urinating.
Frequent urge
Urinary incontinence
Soreness when emptying the bladder
Acute urinary retention
All these manifestations are due to the proliferation of atypical prostate cells. They narrow the prostate urethra, and in some cases completely block it.
With the progression of the tumor process, the organs surrounding the prostate gland can be affected. Most often, the rectum, bladder and regional lymph nodes are affected.
The reliable causes of the development of prostate cancer are still not known. Experts consider hormonal imbalance in older men to be the main factor in triggering the tumor process. Thus, prostate cancer is a hormone-dependent tumor, the inducer of which is testosterone. Other signs of high testosterone levels in men are:
Frequent changes in mood, high levels of aggression.
Baldness that occurs simultaneously with increased hair growth on the trunk.
Weight gain on the background of decreased appetite.
Decreased sexual activity.
Due to the increased risk of prostate cancer in men with high testosterone levels, this group of patients requires regular preventive examinations, at least every six months.
Prostate cancer https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostate_cancer treatment
The main treatments for prostate neoplasms include:
Surgery: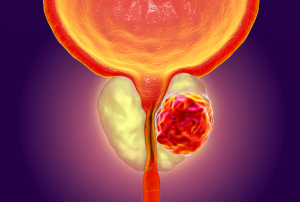
· Radical prostatectomy – removal of the entire prostate gland along with the seminal vesicles.
Robot-assisted prostatectomy
Cryotherapy – exposure of the prostate tissue to extremely low temperatures.
Radiation therapy is the effect of ionizing radiation on tumor and healthy cells, causing irreversible damage to DNA. And also its kind of brachytherapy – the introduction of radioactive elements into the prostate gland.
Chemotherapy – hormone therapy aimed at lowering testosterone levels in the patient’s body
Photodynamic therapy is the use of photosensitizing drugs that have a tropism for atypical cells and the ability to accumulate in them. Under the influence of light waves of a certain wave, such a drug destroys cancer cells without affecting healthy ones. This technique allows you to effectively defeat the disease with minimal side effects.