Cancer of the body of the uterus is a malignant tumor that develops from the cells of the endometrium. The danger of the disease is that it is difficult to diagnose it in the early stages, and as the tumor process spreads, the percentage of 5-year survival decreases. Hormonal disorders, diseases of the reproductive and endocrine systems, endometrial atrophy and other reasons can cause the development of oncology.
Classification
Histological classification includes a division into the following types of malignant tumors of the uterine body:
endometrial adenocarcinoma;
mucinous cancer;
serous adenocarcinoma of the endometrium.
squamous cell carcinoma;
glandular squamous cell carcinoma;
clear cell carcinoma of the endometrium;
leiomyosarcoma;
The following types of endometrial cancer are also distinguished, depending on the structure of the tumor:
Highly differentiated. It has the most favorable forecasts, as it develops slowly.
Moderately differentiated. It is characterized by an average rate of spread of the tumor process.
Poorly differentiated cancer. Differs in rapid progression and the appearance of metastases. It is considered the most aggressive form of oncology.
Stages
Depending on the localization and spread of the malignant tumor, the following stages of uterine cancer are distinguished:
Stage 1. The tumor is localized in the body of the uterus and does not have metastases.
Stage 2. The neoplasm spreads to the cervix, but there is no metastasis.
Stage 3. Cancer cells infect nearby lymph nodes and tissues.
Stage 4. The tumor has distant metastases in the bladder, rectum, bones, liver and other organs.
How does uterine cancer manifest?
Women are most often concerned about these early symptoms of uterine cancer:
uterine bleeding;
leucorrhoea;
discharge of a watery or purulent character;
pulling pains.
The appearance of bleeding in a woman in menopause is a reason to see a doctor. Patients of reproductive age should be evaluated if menstruation is heavy and bleeding or smearing occurs in the middle of the cycle. As the progression progresses, the symptoms intensify, weakness and fatigue are also added.
Every woman should know how to recognize cancer of the uterine body, as well as regularly undergo preventive examinations to prevent the development of the disease and disability.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of cancer of the body of the uterus includes a number of studies:
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
hysteroscopy, colposcopy;
computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
laboratory tests (blood biochemistry, general blood and urine analysis, hormonal and cytological studies, analysis for oncological markers);
PET-CT;
To confirm the diagnosis, curettage or aspiration biopsy may be performed, and the tissue sample taken is sent for histological examination.
Treatment methods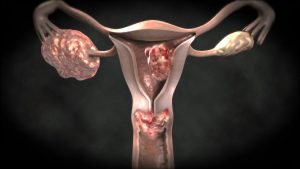
The basis of treatment is almost always the operation, which is combined with other techniques. Most often, a laparoscopic operation is performed, although the type and amount of surgical intervention is determined in each case individually, depending on the prevalence of the tumor process.
Additionally, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used for cancer of the uterine body. They allow you to reduce the neoplasm before the operation and destroy the remains of atypical elements after it.
With a hormone-dependent tumor https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hormone-sensitive_cancer, hormonal treatment for cancer of the uterine body is required. The drugs and their dosages are selected individually. For advanced and inoperable neoplasms, palliative treatment of uterine cancer is carried out in our clinic, aimed at relieving symptoms and increasing life expectancy.
Cancer prevention consists in maintaining a normal weight, moderate physical and sexual activity. It is equally important to identify and eliminate hormonal disorders in a timely manner, to regularly go to the gynecologist for professional examinations.